An alternating current (AC) input feeds AC power into your direct current (DC) power supply. Choosing the right AC input for your power converter or switching power supply is critical for ensuring adequate performance, efficiency, and reliability.
AC input refers to the type of alternative current input power that feeds into the machine. The device then converts the input voltage and input current into a stable DC output. Choosing an AC power source that aligns with your project demands and testing purposes is vital. The input must also be compatible with your DC power supply.
Below, we explore key considerations for choosing an AC input, covering everything from the different types of AC inputs to the way you determine your supply’s voltage range.
AC input refers to the alternating current provided to a DC power supply. The supply converts the AC power into a direct current through a rectification and filtering process within the power supply. The rectifier requires a high-quality AC input to perform efficiently.
Different applications and environments require specific types of AC input power to ensure stable and efficient operation. You must consider not only the AC input voltage but also the waveform, current, amps, and stability of the power being produced. Generally, AC inputs produce power in the square, triangle, and sinusoidal waveforms.
There are several types of AC inputs commonly used in DC power supplies. These include single-phase, three-phase, and universal. Here’s a closer look at each one.
The main types of AC inputs include these three examples:
A single-phase AC input is the most common type of AC power used in residential and light commercial applications. It typically operates at voltages between 100 VAC and 240 VAC. These inputs have a single live wire and a neutral wire. Single-phase AC inputs have key advantages and drawbacks:
Pros:
Cons:
Single-phase AC inputs are ideal for smaller DC power supplies. If your testing requirements demand a relatively low output voltage, consider a single-phase input. However, if you need to engage in high-power testing, you’ll have to invest in a more robust input.
A three-phase AC input has three alternating currents that are out of phase with each other by 120 degrees. You might need a three-phase model if you are working in industrial and high-power applications that require considerable energy. For example, you could use a three-phase AC input to test large equipment or industrial transistors.
Before you invest in a three-phase input, consider its pros and cons, which include the following:
Pros:
Cons:
Three-phase AC inputs are preferred for industrial settings and testing scenarios requiring a substantial amount of power. These inputs have much greater volt and amperage ranges than single-phase options. An increased range also creates a greater risk to your team and equipment, meaning safety must always be a top priority.
A universal AC input refers to power supplies that can accept a wide range of AC voltages, typically from 90 VAC to 264 VAC. These power supplies are designed to operate seamlessly across different voltage standards worldwide. A universal output can offer benefits and drawbacks such as:
Pros:
Cons:
If you are testing devices and equipment designed for global distribution, a universal AC input represents an ideal choice. It ensures your products can operate reliably in different regions without encountering voltage compatibility issues.
Power supplies capable of supplying 3 kW or more will, as a general rule, require some form of three-phase AC power input. Depending on your region and your facility, you may need to connect your EA power supply to three-phase 208 VAC, 380 VAC, 400 VAC or 480 VAC.
In the US, 208 VAC connections are common. Our US208V models have a 5-pole AC connector on the rear of the unit as shown in Figure 1. When connecting the 3-phase AC supply, use the labeling next to the plug (filter housing) to ensure that you connect the phases properly.
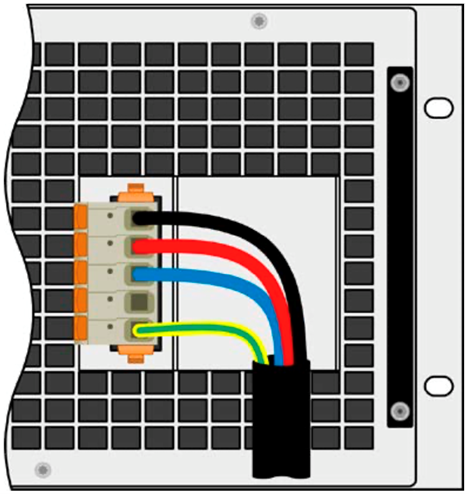
Figure 1: This figure shows how to connect a 208 VAC, 3-phase cable to an EA power supply. The cable shown uses the U.S. color code.
The following connections are required:
| Rated Power | Inputs on AC plug | Supply type | Configuration |
| 15 kW | L1, L2, L3, (N), PE | Three-phase (3P) | Delta |
The PE conductor is necessary and must always be connected! The N conductor, if present in the cable, can be connected to the free position of the AC connector. For a 15 kW power supply, we suggest using a cable with AWG 8 conductors. AWG 8 conductors can handle currents up to 56 A. The AC connector can accommodate loose/soldered conductors up to 16 mm2 (AWG 6).
If your installation requires an input voltage of 380 VAC or more, EA offers what we call Wide Range, or WR, input for most of our high-power, programmable DC power supplies and loads. Power supplies with this feature can accept voltages between 380-480 VAC +/- 10%, making it easier to use these power supplies anywhere around the world. This is very important as most power supply designs do not allow for reconfiguring to different input voltages.
To ensure that you don’t run into problems when installing your EA DC power supply, consult with your facilities management personnel to see what input power is available in your lab or production area before purchasing the supply. Be sure to ask the following questions:
It’s important to put some thought into your choice of AC input. Here are the factors you should consider before making this crucial investment:
Before selecting an AC input for your DC power supply, consider your project’s power requirements and load characteristics. Determine the maximum power you may need for your testing scenarios and ensure the AC input can supply sufficient energy without overloading.
For high-power applications, a three-phase AC input will be the best fit. A single-phase input may suffice for lower power needs and will be more economical.
Choosing a solution that offers optimal efficiency will help keep your operating costs down. A three-phase input tends to be more energy-efficient, reducing energy losses and heat generation.
Evaluate the efficiency ratings of different AC input types and choose one that offers optimal performance for your specific application. Balance power requirements, operational efficiency, and your intended use.
If you aren’t sure which option will fit best, connect with EA. You can discuss your project requirements with one of our experienced team members.
Think about where you’ll be using your power supply and AC input. Factors that can impact your power supply’s performance and longevity include:
Ensure that the chosen AC input type can withstand these conditions and provide reliable operation over time.
Budget must always be top of mind. If you can keep your operating and equipment costs low, you’ll be able to conduct more thorough testing and improve product quality.
Three-phase AC inputs offer higher efficiency and power capacity. They also come with higher installation and maintenance costs. Universal AC inputs provide versatility but can be more expensive due to their advanced design.
Balance the initial investment with long-term operational costs and benefits. Choose the most economical solution to meet your current intended use case without compromising long-term needs.
Here are a few more factors to account for to ensure your AC input supports your project needs:
Begin by thoroughly assessing your power supply needs, including the maximum power load, voltage requirements, and operational environment. Understand the characteristics of your load and the demands it places on the power supply.
For instance, if you are using a bidirectional DC power supply, ensure your AC input can accommodate the power conversion process and provide stable power. Fluctuations in power input can negatively impact the supply’s performance and functionality.
You must match the AC input type and capabilities to your application’s specific requirements. For example, an autoranging DC power supply has different input requirements than a low-output power converter. For residential or small commercial applications, a single-phase AC will typically suffice.
For simplicity’s sake, consider purchasing your DC power supply and AC input from the same provider. Elektro Automatik can ensure your input and power supply components are compatible and optimized for performance. Our hands-on approach takes the guesswork out of choosing testing components.
There aren’t any one-size-fits-all AC inputs. Consider factors such as:
A three-phase or universal AC input may be more expensive, but the long-term efficiency and versatility benefits help provide a strong return on investment. Choose the option that best aligns with your current needs and that has the most potential for long-term usefulness.
An AC input refers to the alternative current provided to the power supply unit. The unit then converts the AC input into direct current output. There are three main types of AC inputs: single-phase, three-phase, and universal. You need a high-quality, stable input to keep your DC power supply operating efficiently.
The AC input you select will have a direct impact on your DC power supply’s efficiency and performance. The correct input can reduce energy loss and improve stability. It will also extend your power supply’s lifespan while providing you with adequate input to run all necessary tests.
Your AC input will also have a profound impact on the overall cost of operating your power supply. By proactively reducing operating costs by selecting the right AC input, you can free up additional funding and resources to support your testing processes.
Consider factors such as your power supply’s maximum power load and voltage requirements. Also, be mindful of the operational environment.
Evaluate the efficiency and performance characteristics of different AC input types and match them to your specific application requirements. Consider long-term operational costs and benefits to make an informed decision.
And if you need an objective perspective, connect with EA. Our experienced team can help you evaluate your project needs and make targeted recommendations to ensure your equipment aligns with your intended use case.
A single-phase AC input uses a single alternating current and makes sense in lower-power applications. They are simple to install and maintain. Single-phase units are also cost-effective.
A three-phase AC input uses three alternating currents that are out of phase with each other. The more complex arrangement provides greater efficiency and power capacity for industrial and high-power applications. The choice between single-phase and three-phase depends on your specific power requirements and application environment.
Universal AC inputs are designed to operate across a wide range of voltages. However, they may not always be the most efficient choice for every application. Just because you can use them for almost any application doesn’t mean you should.
Generally, consider universal AC inputs if you are testing equipment that will be used in global markets. If you need an input for low-voltage applications, consider a single-phase input, and if you require a high-power output, consider a three-phase unit.
